SPACE / AEROSPACE
PLX has been producing space-qualified instruments and components for over 40 years and cover a wide range of applications.
- Space / Aerospace Applications
- Mapping and Topography
- Environmental and Atmospheric
- Scientific
- Laser Communication
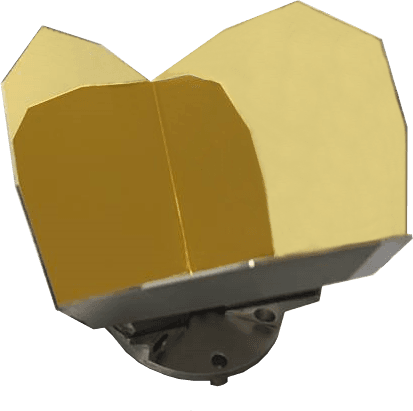

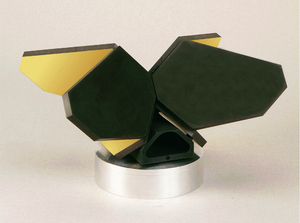


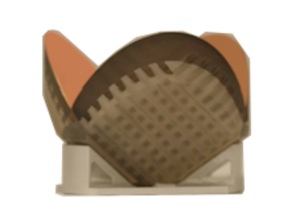
PLX was involved with the European Space Agency (ESA) for their Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) project through Thales Alenia Space, launched in December 2022. MTG is a series of next-generation meteorological satellites that will provide crucial weather and climate data for Europe and Africa. PLX provided a pair of 101mm clear aperture beryllium retroreflectors for the interferometer of the Infrared Sounder. Beryllium was chosen for its low weight and high stiffness, which are important as the interferometer modulates the mirror position.
The latest example is our Retroreflectors operating in the TIRVIM (Thermal Infra-Red V-Shape Interferometer Mounting) Spectrometer, which is part of the Atmospheric Chemistry Suite (ACS), launched in March, 2016 and is now successfully operating in orbit around Mars.
Some examples include RIS which is the largest Retroreflector ever sent into space as well as Beryllium assemblies for the Thermal Emission Spectrometer (TES) built by JPL for NASA.
Our Retroreflector Array™ for NASA’s Endeavor Shuttle Radar Mission  Retroreflector Array helped create a high-resolution database of the earth. PLX’s space qualified retroreflectors are part of the most recent experiments to measure the atmospheric conditions on Earth, Mars and Venus.
Retroreflector Array helped create a high-resolution database of the earth. PLX’s space qualified retroreflectors are part of the most recent experiments to measure the atmospheric conditions on Earth, Mars and Venus.
Recently we’ve designed hard mounted retroreflectors using Invar for the Canadian Astro-H Metrology System (CAMS) for their space based X-ray observatory, as well as a vacuum-compatible Lateral Transfer Hollow Retroreflector for ICESAT-2, NASA’s Ice, Cloud and Land Elevation Satellite scheduled for launch in 2017.
Celebrating 40 years in space.
PLX’s space heritage dates back to July 1975 when the company provided hollow retroreflectors to the Apollo-Soyuz Russian-American space hookup program. The units were used in the docking procedure to align the two vehicles. The program included both joint and separate scientific experiments and provided useful engineering experience for future joint US–Russian space flights, such as the Shuttle–Mir Program and the International Space Station.
For more information, please visit our contact us page
